Chloroplasts & Mitochondria: The Energy Powerhouses of Biology
- Tech Team
- Jan 5
- 4 min read
Why Energy Is Essential for Life All living organisms require energy to survive and function. At the cellular level, energy is needed for processes such as growth, repair, movement, active transport, and cell division. Without a constant energy supply, cells would stop working, and life would not be possible. However, energy from sunlight or food cannot be used directly by cells. It must first be converted into a usable form. This conversion happens inside specialized organelles that handle energy transformation efficiently. This is where chloroplasts and mitochondria play their most important role in sustaining life.
What Are Organelles?
Organelles are specialized structures inside cells that perform specific functions, much like organs in the human body. Each organelle has a particular role that helps the cell survive and work efficiently. For example, the nucleus controls cell activities, ribosomes make proteins, and vacuoles store materials. Among all organelles, chloroplasts and mitochondria are unique because they manage energy. They do not just store substances—they convert energy from one form to another, which is essential for life on Earth.
Chloroplasts—Capturing Energy from Sunlight Chloroplasts are organelles found only in plant cells and some algae. Their main function is to perform photosynthesis, a process that allows plants to make their own food using sunlight. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun. This energy is then converted into chemical energy stored in glucose. This stored energy becomes the foundation of most food chains and supports almost all living organisms directly or indirectly.
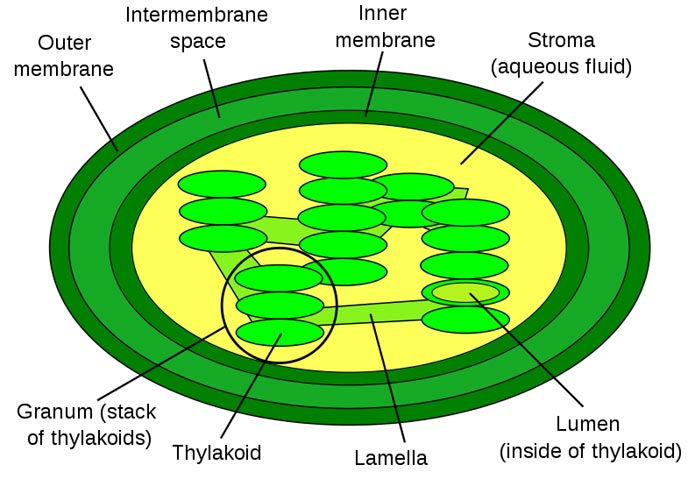
Structure of a Chloroplast: The structure of a chloroplast is closely related to its function. It has a double membrane that protects the organelle and controls what enters and exits. Inside the chloroplast is a fluid-filled region called the stroma, where glucose is formed during photosynthesis. Within the stroma are flattened sacs known as thylakoids, which are stacked into structures called grana. The thylakoids contain chlorophyll and are the site where light energy is absorbed. This organized structure allows photosynthesis to occur efficiently.

Photosynthesis—Step-by-Step Explanation:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Word equation: Carbon dioxide + Water + Light energy → Glucose + Oxygen
First, chlorophyll absorbs light energy. This energy is used to split water molecules and provide energy for chemical reactions. Carbon dioxide from the air then combines with hydrogen to form glucose. Oxygen is released as waste. The glucose produced is either used immediately for energy or stored as starch for later use.

Mitochondria—Releasing Energy for Cell Activities
Mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells and are responsible for cellular respiration. Their main role is to release energy stored in glucose so that the cell can use it.
Because mitochondria provide energy needed for almost all cell activities, they are often called the powerhouse of the cell. Cells that need more energy, like muscle cells, contain more mitochondria.

Structure of a Mitochondrion A mitochondrion has an outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane. These folds are called cristae, and they significantly increase the surface area available for chemical reactions. Inside the inner membrane is a fluid-filled space called the matrix, which contains enzymes needed for respiration. The folded structure allows mitochondria to produce large amounts of energy efficiently, which is essential for active cells.
Cellular Respiration—How Energy Is Released Cellular respiration is the process by which energy stored in glucose is released in a controlled manner. Word equation: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP) During respiration, glucose is broken down step by step in the presence of oxygen. This releases energy gradually instead of all at once. The released energy is used to produce ATP, while carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products.
ATP—The Energy Currency of Cells ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the cells' immediate energy source. It acts like a rechargeable battery that powers cellular activities such as movement, synthesis, and transport. Mitochondria produce ATP during respiration, and cells use ATP whenever energy is needed. Without ATP, even basic cell functions would stop. This is why ATP is often described as life's energy currency.
10. Chloroplasts vs Mitochondria (Detailed Comparison)
Feature | Chloroplast | Mitochondria |
Found in | Plant cells only | Plant & animal cells |
Main role | Energy storage | Energy release |
Process | Photosynthesis | Cellular respiration |
Energy type | Light → Chemical | Chemical → ATP |
Output | Glucose, oxygen | ATP, CO₂, water |
Energy Flow: Linking Photosynthesis & Respiration Photosynthesis and respiration are interconnected processes that maintain energy balance in ecosystems. Chloroplasts capture sunlight and store energy in glucose. Mitochondria use that glucose to produce ATP. This creates a continuous energy flow: Sunlight → Glucose → ATP Plants act as producers, while animals depend on plants directly or indirectly. This relationship explains why energy flow is central to all living systems.
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells Plant cells contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria, allowing them to make and use energy. Animal cells contain only mitochondria, meaning they rely on plants for energy-rich food. This difference explains why plants are self-feeding (autotrophs) and animals are dependent on others (heterotrophs).
MYP Exam Tips & Common Mistakes
Always link structure to function
Write full word equations when asked
Avoid confusing respiration with breathing
Use diagrams wherever possible
Compare organelles clearly in tables
Conclusion Chloroplasts and mitochondria are essential for life because they manage how energy is captured, stored, and released in cells. Chloroplasts store energy from sunlight, while mitochondria release that energy for use. Together, they explain the complete journey of energy in living organisms. For MYP 4 & 5 students, this topic builds a strong base for understanding ecosystems, metabolism, and human biology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Do animal cells have chloroplasts?
No, only plant cells and some algae contain chloroplasts.
2. Why do plant cells need mitochondria?
Plants also need ATP for growth and repair.
3. What is the role of cristae?
They increase surface area for ATP production.
4. Is respiration the same as breathing?
No, respiration is a cellular process.
5. Is this topic important for MYP assessments? Yes, it is a core concept tested regularly.




Comments